power plant
Power Plant: The Beating Heart of the Power Industry
Power plants are considered critical infrastructures for the reliable supply of electric power, serving as the cornerstone of every country’s economic, industrial, and social development. Sustained electricity production and the ability to meet the growing energy demands of modern societies rely heavily on the effective and principled management of various power plant components. Every modern power plant consists of several main sections and vital auxiliary systems—collectively known as the Balance of Plant (BOP)—which operate in precision to guarantee uninterrupted power generation and transmission.
- Main Components of a Power Plant
- a) Turbine & Generator
- Turbine: Responsible for converting the chemical or thermal energy of fuel into mechanical energy.
- Generator: Converts the mechanical energy from the turbine into electrical energy.
- Common Types: Steam Turbine, Gas Turbine, Combined Cycle.
- b) 6.6kV Switchgear
- This is the Electrical Control & Protection Center for the plant’s internal equipment.
- Includes circuit breakers, disconnectors, and measuring equipment for isolation, protection, and monitoring.
- c) High Voltage Substation
- Steps up the output voltage of the generator to transmission-level voltages and enables connection to the national grid.
- Comprises step-up transformers, protection systems, and power switches.
- d) Main Transformers
- Manage voltage conversion and long-distance transmission to minimize power losses.
- Equipped with advanced protection like Buchholz relays and modern cooling systems.
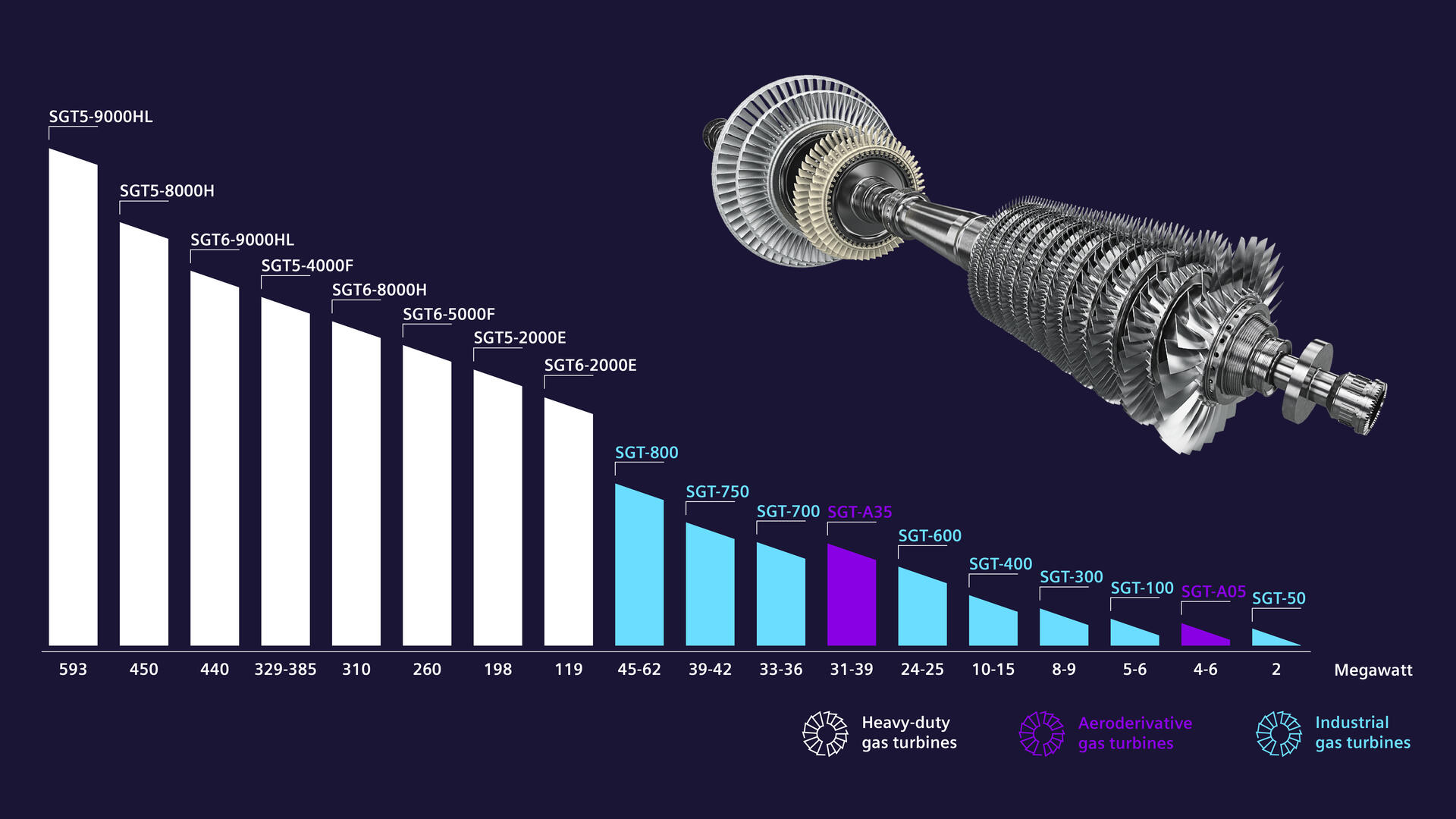
- Key Balance of Plant (BOP) Systems
The BOP consists of a broad suite of support systems and equipment that ensure the safe, stable, and efficient operation of the power plant:
- Firefighting System: Fire detection and extinguishing equipment to safeguard the facility.
- Fuel Storage Tanks & Fuel Pumps: Safe storage and secure supply of fuel to user units, with continuous monitoring.
- Gas Reducing & Metering Station (GRMS): Gas pressure regulation, equipped with flow and pressure monitoring for quality and safety.
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) Water Treatment Plant: Supplies high-purity water for boilers, preventing scale and corrosion.
- Compressed Air Station: Provides compressed air for instrumentation, controls, and pneumatic systems.
- Diesel Generator Room: Emergency diesel generators supply backup power for essential systems during blackouts.
- Heller Cooling Towers: High-efficiency cooling towers improve the cooling process and reduce raw water consumption.


- Benefits of Advanced Technologies in Power Plants
- Efficiency & Productivity Improvement
- Enhanced Operational Stability & Reduced Sudden Outages
- Smart Resource Management
- Lower Operational Costs
- Extended Equipment Lifetime
- Enhanced Safety & Environmental Protection
- The Role of Regular Maintenance
Proper and scheduled maintenance, supported by international standards (such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001, OHSAS 18001/ISO 45001), is vital for ensuring continuous, safe, and optimized plant performance under varied operational and environmental conditions. This leads to increased reliability and operational readiness at all times.
Conclusion:
With meticulous technical design and the adoption of state-of-the-art technologies across all sections, power plants ensure a reliable, safe, and cost-effective electricity supply for society—securing a bright future for the power industry.
Energy demand drivers
- Affordable and reliable energy fuels economic development and modern living standards.
- Large energy disparity still exists between developed and developing countries.
- Growing energy consumption supports economic expansion, enabling longer, more productive lives for the growing global population.
More than 4 billion people live below modern standards for life expectancy, education, and income
U.N. Human Development Index
2022 Index
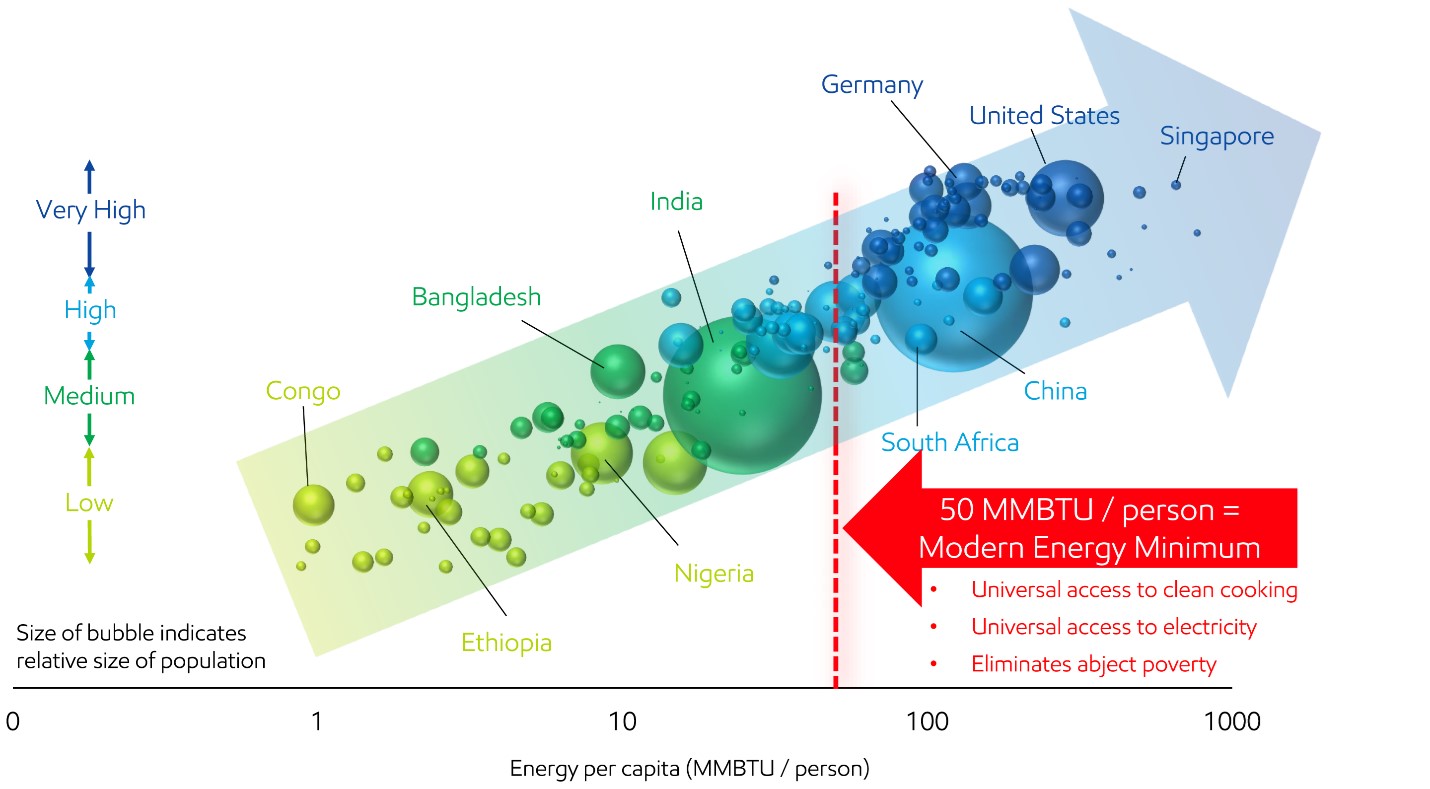
Source (see reference list): U.N. Human Development Reports, EIA, ExxonMobil analysis
Energy improves quality of life.
- Rising energy use fuels higher incomes that enable people to own homes, purchase labor-saving appliances, travel, and obtain needed medical services.
- The United Nations Human Development Index is a measure of average quality of life by country, based on life expectancy, education, and income.
- Consumption of 50 million British thermal units (MMBTU) per person is the threshold needed to materially move the human development indicators; however, today, more than 4 billion people live in countries below the “modern energy minimum.”

Population
OECD: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, a group of more affluent democracies with market-based economies that promotes economic growth.
GDP
OECD: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, a group of more affluent democracies with market-based economies that promotes economic growth.
Purchasing power per person
OECD: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, a group of more affluent democracies with market-based economies that promotes economic growth.
By 2050, population is expected to grow by nearly 2 billion people as GDP doubles.
- Developing countries’ income doubles to $25,000 but remains well below developed-country levels.
